The most important thing in it is network .Without network , we cannot send data to the internet . Every computer that connect to the internet is a part of network .
Internet Protocol : IP address
Every machine on the internet has it own Internet Protocol address . IP address is a language that computers use to communicate with the internet .For an example , IP address is like 216.27.22.162. It normally expessed in decimal number form . The four number for every of it was called octet . Octet act as to create classes that can be assigned to differentiate an address such as it was for goverment , organization and others . It was split into two thing , host and network . The Network section always contains the first octet. It is used to identify the network that a computer belongs to. Host sometimes referred to as Node is identifies the actual computer on the network. The Host section always contains the last octet..
IP address can be classified into several classes such as ...
Class A
Class A addresses are assigned to networks with a very large number of
hosts. The high-order bit in a class A address is always set to 0. The
next seven bits (completing the first octet) complete the network ID.
The remaining 24 bits (the last three octets) represent the host ID.
This allows for 126 networks and 16,777,214 hosts per network.
Class B
Class B addresses are assigned to medium-sized to large-sized networks. The two high-order bits in a class B address are always set to binary 1 0. The next 14 bits (completing the first two octets) complete the network ID. The remaining 16 bits (last two octets) represent the host ID. This allows for 16,384 networks and 65,534 hosts per network.

Class C
Class C addresses are used for small networks. The three high-order bits
in a class C address are set to binary 1 1 0. The next 21 bits
(completing the first three octets) complete the network ID. The
remaining 8 bits (last octet) represent the host ID. This allows for
2,097,152 networks and 254 hosts per network. 

Class D
Class D addresses are reserved for IP multicast addresses. The four high-order bits in a class D address are always set to binary 1 1 1 0. The remaining bits are for the address that interested hosts recognize. Microsoft supports class D addresses for applications to multicast data to multicast-capable hosts on an internetwork.
Class D addresses are reserved for IP multicast addresses. The four high-order bits in a class D address are always set to binary 1 1 1 0. The remaining bits are for the address that interested hosts recognize. Microsoft supports class D addresses for applications to multicast data to multicast-capable hosts on an internetwork.
Class E
Class E is an experimental address that is reserved for future use. The high-order bits in a class E address are set to 1111.
The
network ID cannot begin with the number 127. The number 127 in a class A
address is reserved for internal loopback functions. For example, 127.0.0.1 is the common loopback address.
·
Loopback
means the interface created and designated to test a local port or interface.
It routes test messages from their source device back to the source without any
processing or modification.
·
The loopback IP address is the
address used to access itself. A loopback interface is also known as a virtual
IP, which does not associate with hardware interface.
·
The loopback address is used to test
network software without physically installing a Network Interface Card (NIC), and without having to
physically connect the machine to a TCP/IP network.
Domain Name System
Although people can type address information like http://207.241.148.80/ into their Web browser to visit sites, being able to use proper names like http://www.hotmail.com/ is much more practical. When someone types a site's name into their browser, DNS looks up the corresponding IP address for that site, the data required to make the desired network connections between Web browsers and Web servers.
The DNS organizes its servers into a hierarchy. For the Internet, so-called root name servers reside at the top of the DNS hierarchy. The Internet root name servers manage DNS server information for the Web's top-level domains (like ".com" and ".uk"). Servers at the next lower level of the DNS hierarchy track second-level domain names and addresses (like "hotmail.com").
Hierarchy of domain names
ISP
Short for Internet Service Provider, it refers to a computer access to
the Internet. The service provider usually provides a software
package,username and password. You can then log on to the Internet and
browse the World Wide Web and send and receive e-mail. ISPs also serve
large companies, providing a direct connection from the company's
networks to the Internet. ISPs.An ISP is a company that provides individuals and other companies access to the Internet and other related services such as Web site building and virtual hosting. An ISP has the equipment and the telecommunication line access required to have a point-of-presence on the Internet for the geographic area served. The larger ISPs have their own high-speed leased lines so that they are less dependent on the telecommunication providers and can provide better service to their customers.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
There are three important things about HTTP of which you should be aware:
·
HTTP
is connectionless: After a request is made, the client disconnects from the
server and waits for a response. The server must re-establish the connection
after it process the request.
·
HTTP
is media independent: Any type of data can be sent by HTTP as long as both the
client and server know how to handle the data content. How content is handled
is determined by the MIME specification.
·
HTTP
is stateless: This is a direct result of HTTP's being connectionless. The
server and client are aware of each other only during a request. Afterwards,
each forgets the other. For this reason neither the client nor the browser can
retain information between different request across the web pages.
The diagram shows where HTTP Protocol fits in communication:


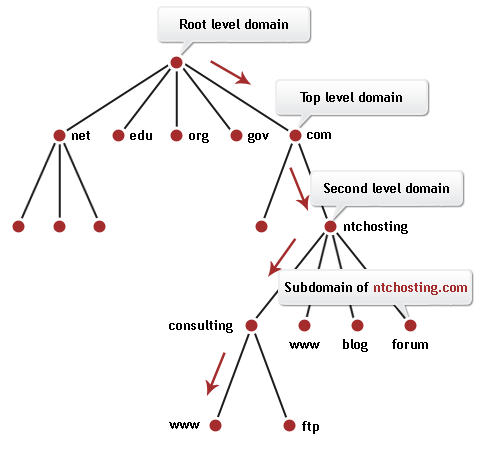



 Fig. 4. BNC connector
Fig. 4. BNC connector